Chillers play a key role in keeping industrial processes and buildings running smoothly. Their efficiency directly affects energy consumption and operational costs. This is why it is important to monitor chiller systems and calculate their efficiency correctly. One of the most widely used methods to measure efficiency is the Coefficient of Performance (COP). In this article, we will explain how the COP of industrial chillers is calculated, how it relates to other efficiency formulas, and how performance can be optimized.
Before learning about COP, it is important to understand what chiller efficiency means. Chiller efficiency shows how well a system converts electrical energy into cooling capacity. It is usually expressed in two ways: kW/ton, which measures how much power is used per ton of cooling, and COP, which is the ratio of cooling output to energy input. A more efficient chiller consumes less power while producing the same or greater cooling capacity.
One common way to measure performance is with the chiller efficiency formula in kW/ton. The calculation is simple:
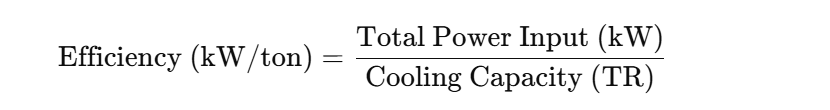
For example, if a chiller consumes 500 kW of electricity to provide 200 tons of refrigeration (TR), the efficiency is 2.5 kW/ton. In this case, the lower the number, the better the performance. High-performing chillers usually operate below 0.7 kW/ton under ideal conditions.
The COP in HVAC is another common way to measure efficiency. The formula is:

For example, if a chiller produces 2,500 kW of cooling while consuming 460 kW of electricity, the COP is 5.4. This means that for every 1 kW of electricity used, the system provides 5.4 kW of cooling. A higher COP value always indicates better efficiency and lower energy costs.
To fully understand efficiency, it is also important to know how to calculate TR (Tons of Refrigeration). The formula is:
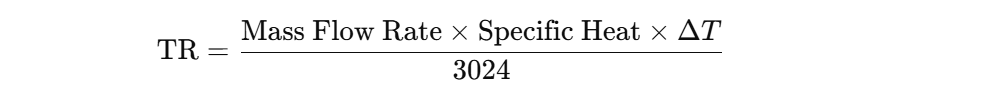
This formula helps determine the cooling capacity of a chiller system. Accurate TR calculations are necessary to size equipment correctly and to compare performance with the chiller manufacturer’s design specifications.
Another useful efficiency metric is IKW (Input kW per TR). The formula is similar to kW/ton:

If a chiller consumes 300 kW of energy to provide 100 TR, the IKW is 3.0. As with kW/ton, lower values indicate better energy efficiency. For modern high-performance chiller systems, IKW values should be as low as possible, ideally under 0.6 kW per ton.
Chiller efficiency is also influenced by the condenser approach temperature. This is the difference between the condensing temperature and the cooling water outlet temperature. The formula is:
Approach Temperature=Condensing Temp−Cooling Water Outlet Temp
A lower condenser approach temperature means better heat transfer and higher overall efficiency. For example, if the condensing temperature is 105°F and the cooling water outlet temperature is 95°F, the approach is 10°F. Keeping this value low helps the chiller run more effectively.
While the formulas are straightforward, real-world COP values can change depending on operating conditions. The main factors include:
Cooling load: Conventional single-speed chillers reach maximum COP at full load, but most systems run at part load for most of the year.
Ambient conditions: Outdoor temperature and water quality affect performance.
Equipment design: Compressors, heat exchangers, and refrigerants all influence efficiency.
Maintenance: Dirty coils, low refrigerant levels, or blocked water flow reduce COP.
Understanding these factors allows operators to spot inefficiencies quickly.
Improving efficiency is not only about design but also about proper operation. Here are proven methods to optimize chiller COP:
Use Variable Speed Drives (VSDs): These adjust compressor speed to match load demand and reduce power use at part load.
Perform regular maintenance: Cleaning coils, checking refrigerant charge, and ensuring water flow improves performance.
Optimize cooling tower operation: Balanced water flow helps maintain stable condenser approach temperatures.
Choose energy-efficient refrigerants: Newer refrigerants reduce power demand and improve cooling output.
Monitor system performance: Regularly check kW/ton, COP, and IKW to track efficiency over time.
Understanding how to calculate chiller efficiency with formulas like COP, kW/ton, IKW, and TR helps operators and engineers keep systems running at peak performance. By monitoring these values and applying optimization strategies, businesses can lower operating costs, extend equipment life, and achieve greater energy savings.
Kaydeli has been committed to delivering advanced and reliable solutions for industrial cooling for decades. As a professional chiller manufacturer, Kaydeli provides high-quality systems designed to achieve excellent efficiency and stable operation. If you are looking for dependable chiller solutions, Kaydeli is your trusted partner in energy-efficient cooling.
By continuing to use the site you agree to our privacy policy Terms and Conditions.